computerist
Municipal State Institution "SOSH No9"
Republic of Kazakhstan, Pavlodar region, Ekibastuz
Contents
Lesson 1
Subject:Safety and workplace organization in the computer science office
Class: 1-11
Equipment:handout, PC, presentation to the lesson
Class type:TB introduction.
Form of organization of educational activities:novelty
Abstract:This lesson is intended for pupils of grades 1-11 of secondary schools, for an introductory lesson on Safety Techniques and organization of the workplace in the computer science office. The lesson was developed on the basis of GOSO RK.
Objective of the lesson:
- educational:Acquaint students with the rules of conduct in the office of VT.
- Educational:It teaches students skills and skills.
- developing:Develop proper behavior in the VT office (Slide 2)
Lesson plan:
1. Organizational moment /3 min/
2. Explanation of a new topic /25 min/
3. Fixing of new material /10 min/
4. Homework /2 min/
5. Summary/5 min/
Class progress:
1. Organizational moment
Welcome, student mark. A brief description of the practical work, its goals, the progress of implementation.
2. Explanation of a new topic
Instructions for training and instruction of students on occupational safety
- In order to educate students of a conscious attitude and assimilation of correct and safe methods and techniques of work, teachers are obliged to instruct and train students on compliance with occupational safety and health requirements.
- Instruction and training on labor protection are carried out with all students at the introductory lesson in the office, and then before practical work on the PC.
- At the introductory briefing, the teacher should familiarize students with the rules of occupational safety and health; with dangerous moments that can be encountered in the process of work, and with appropriate precautions.
- Introductory instruction is conducted by the head of the study (teacher) in the form of a lecture, conversation.
- Instruction before work on PC (primary at the workplace) complements the introductory instruction and is aimed at acquainting students with the requirements of proper organization and maintenance of the workplace, with safe working methods and rules for the use of protective equipment, with possible dangerous moments in the performance of a particular job, with the duties of the employee at his workplace, as well as dangerous situations and rules of behavior when they occur.
- All information on conducting instruction of students is recorded in the class journal.
1. Basic provision
Before using computer technology in the educational process, all students should be instructed on safety, familiarize themselves with the rules of behavior in emergency situations, methods of first aid in case of electric shock and exercises to relieve visual stress and fatigue. After the instruction, students must receive a credit for knowledge of safety, which is registered in the journal of the appropriate form.
Requirements for labor protection during classes in computer rooms that students should know include safety rules, rules of behavior in the computer classroom, first aid techniques for electric shock, exercises but the removal of visual tension and general fatigue.
2. Safety regulations
Safety regulations can be divided into the following points:
- Common.
- Before I started working on the PC.
- While working.
- In emergency situations.
- At the end of the job.
General safety requirements
- It is forbidden to touch wires, plugs, sockets, plugs, move equipment without the permission of the teacher.
- You cannot enter or leave the classroom without the teacher’s permission.
- You can't go to class without the teacher's permission.
- You can not work on a PC with wet hands and wet clothes.
- It is forbidden to work on PCs that have a violation of the integrity of the housing or wires.
- It is forbidden to put on the table next to the PC briefcases, bags, books. Only pens and notebooks should be placed on the table.
- You can't put anything on the keyboard.
- In the computer classroom, it is forbidden to run, play, distract comrades, engage in outside work. (Slide 4)
Security requirements before starting work on PC
- When power is turned off, inspect the PC and make sure that there is no violation of the isolation and integrity of the PC body and wires.
- Pay attention to whether the wires hang so that it is possible to touch them during work.
- Make a note in the Workplace Use Journal (see annex 1). (Slide 5)
Security Requirements While Working on PC
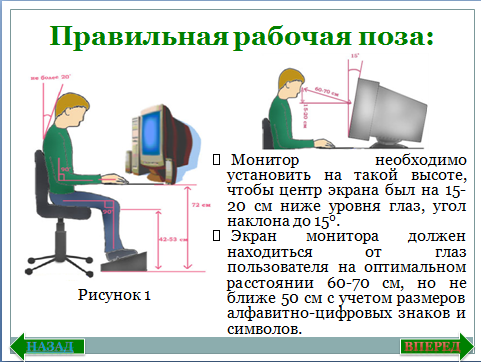
- When working on a computer, it is necessary to observe the optimal distance of the eyes from the screen (60-70 cm). Allowable distance -50 cm.
- Students should not get up when visitors enter.
- In case of visual tension or fatigue, you can perform several exercises without getting up from your seat to relieve tension or fatigue. (Slide 7)
- Students should know first aid techniques for electric trauma, fire extinguisher techniques and fire extinguishing techniques. (Slide 6)
Safety requirements in emergency cases
- If defects of the PC are detected in the process of work, the appearance of burns or unusual sounds, it is necessary to immediately stop working on the PC, turn off the equipment and inform the teacher.
- If necessary, help in extinguishing the fire.
- If necessary, be able to provide first aid to victims of electric current.
- You should know that you can not extinguish a fire in a computer classroom with water. You can use sand or a foam fire extinguisher.
- It is necessary to know that if the victim is under the influence of electric current, then he can not be touched with his bare hands. You can release the victim using materials that are not conductors of electric current. (Slide 9)
Security requirements at the end of work on the PC
- At the instruction of the teacher to disconnect the equipment.
- Clean up the workplace.
- Make a note in the Workplace Accounting Journal (Annex 1). (Slide 10)
A teacher for students conducts a warm-up: "Who answers the questions faster" (Slide 11)
3. Consolidation of new material
The teacher to test this task can use 2 options for testing knowledge.
Option 1:distribute handouts in A4 format. Students must complete the task with colored pencils.
Option 2:Practical PC task. Work in the graphic editor Paint.
View the "Instruction card for task number 1"
Task 1. Turn green on what to do.Maybe.And red is what to do.NOW.
| Enter the computer science office without the teacher's permission. | Entering the computer class calmly. Occupy your workplace. | To be in the computer science office in outer clothes. |
| Make sure there are no visible computer malfunctions. | Push at the door when entering the computer classroom. | If a computer malfunction is detected, inform the teacher. |
| Touch the connector wires. | Start working on the computer only after the permission of the teacher. | Touch the power wires. |
| Bring CDs and floppy disks from other computers to class. | Try to eliminate the detected malfunction of the computer. | Include games or other programs that are not related to the lesson. |
| Working on a computer with dirty hands. | Press the keys gently, without much hitting. | Touch the screen and back of the monitor. |
| Press the keys of the keyboard only when the voltage is on. | Work on a computer in wet clothes or with wet hands. | The distance from the eyes to the monitor screen should be 60-70 centimeters. |
| Put things on the components of the computer. | At the end of the work, put the workplace in order. | Delete files and folders without the teacher’s permission. |
- Receptions of first aid
Assistance with electric shock
- Turn off the current (turn off the switchboard on the switchboard).
- Release the victim from the impact of current (wire), using improvised
- means that are not conductors of electric current.
- Examine the victim and help him depending on the severity of the defeat. Call a doctor (from the school medical center, “ambulance” by phone 103 or from the nearest medical institution). (Slide 12)
Assistance for burns
- Place the affected area under cold water, previously wrapped with cellophane, so that microbes do not get to the surface of the wound.
- Put an aseptic bandage on the burnt place
- Call a doctor (from the school infirmary, "ambulance" on 103 or from the nearest medical institution.) (Slide 14)
Assistance for fainting
- Put the victim on a flat surface on his back, turning his head on his side.
- Call a doctor (from the school medical center, ambulance by phone 103 or from the nearest medical institution). (Slide 15)
Assistance in stopping breathing
- Check the position of the tongue in the mouth, if it fuses - hand to return the tongue to normal position.
- Call a doctor (from the school medical center, "ambulance" by phone 03 or from the nearest medical institution).
- Do artificial respiration (mouth to mouth) until breathing is restored or doctors arrive. (Slide 16)
Securing material
Tasks 2.Set the order of action when providing first aid to the victim in case of electric shock, connecting them sequentially.
| 9. Send the victim to a doctor (or ask a doctor). | 8. If the skin is damaged, treat this place with green or alcohol, apply sterile bandage. |
5. Pay attention to breathing and cardiovascular system. |
| 1. Turn off the current quickly. | ||
| 4. Release the victim from the wires with precautionary measures. | 6. In case of respiratory arrest, start indirect heart massage and artificial respiration | |
| 2. Wear rubber gloves or wrap your hands in a dry cloth. | 3. Stand on a rubber mat or on a dry board. | |
| 7. With the weakening of cardiac activity and breathing, provide access to fresh air, let you smell ammonia and give 25 drops of cardiamine. A pat on the cheeks. |
Additional mission 3.
- The question for students on what points can be divided into safety rules?
- Homework.
- Learn the general safety requirements
- Draw a TB poster.
- Conduct of outcomes
Evaluate the work of the class and name the students who distinguished themselves in the lesson.
Commenting and evaluating.
Literature:
- Computer science. Didactic material. Workshop: For the 7th grade of educational school N. Yermekov, E. Cousin, L. Krepp, S. Pilipenko. – Almaty: Atamur, 2003.


{module Google_kvadrat}
Annexes:
1. Lesson summary (.dox)
2. Presentation (.pptx)
3. Distribution material(.docx)
4. Accounting notebook using PC(.docx)
Download full lesson summary with PowerPoint presentation, volume of 2.1 Mb